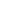
The Splendor of Hanfu in the Qing Dynasty:A Study on the Traditional Dress of Women
In the late imperial era of China, the Qing Dynasty (1644-1912) witnessed a unique blend of cultural and artistic expressions that enriched the lives of its people. Among these, the traditional dress of women, particularly those wearing Hanfu, was a remarkable aspect that reflected the societal norms, cultural values, and fashion trends of the time. This article delves into the world of Hanfu worn by women in the Qing Dynasty, examining its intricate designs, patterns, and the cultural significance it held.

The Hanfu, originating from the Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD), was a traditional Chinese clothing that underwent numerous transformations throughout history. In the Qing Dynasty, it underwent significant changes influenced by the Manchu ruling class and their own traditional costumes. However, the Hanfu persisted as a symbol of cultural continuity and identity for many Chinese women.
The design of Hanfu in the Qing Dynasty was intricate and complex. It often featured a long robe called a chao-yi or chao-shang that was worn over a long under-robe. The robe was usually embroidered with intricate patterns and designs that reflected the wearer’s status and taste. The use of vibrant colors and intricate patterns was common, with symbols like flowers, birds, and clouds often featured in the designs. The sleeves of Hanfu were also an important aspect as they often featured elaborate designs and patterns that added to its beauty.
The cultural significance of Hanfu in the Qing Dynasty was immense. It was not just a piece of clothing; it was a symbol of identity and continuity. Many women wore Hanfu as a way to connect with their ancestors and traditional values. It was also a way to show respect to society and the ruling class. The intricate designs and patterns of Hanfu reflected the wearer’s status in society and were often used as a way to show off their wealth and status.
Another important aspect of Hanfu in the Qing Dynasty was its adaptability. Despite being a traditional dress, Hanfu underwent changes to adapt to the changing times and fashion trends. This adaptability made it possible for women to wear Hanfu even during different occasions and events without compromising on its traditional values or cultural significance.
The influence of Western fashion also reached China during the late Qing Dynasty, but Hanfu continued to hold its own as a traditional dress that was worn on special occasions like weddings, festivals, and other ceremonial events. The fusion of traditional Chinese elements with Western fashion trends gave rise to new styles of Hanfu that were both traditional and modern at the same time.
The role of women in society during the Qing Dynasty was also reflected in their attire. Women were often confined to their homes and were not allowed to participate in many social activities. However, their attire, especially Hanfu, became a medium through which they could express their individuality and creativity. By embroidering their Hanfu with intricate designs or choosing vibrant colors, women could show their unique taste and style even within the confines of their homes.
Today, Hanfu has made a comeback as a fashion trend that is worn by both men and women across China and other parts of the world. The intricate designs, patterns, and cultural significance of Hanfu continue to attract people who want to connect with their Chinese roots or appreciate traditional Chinese culture. The story of Hanfu in the Qing Dynasty is not just about fashion; it is about a rich cultural heritage that continues to inspire people even today.
In conclusion, Hanfu in the Qing Dynasty was not just a piece of clothing; it was an embodiment of cultural values, societal norms, and fashion trends. The intricate designs, patterns, and adaptability of Hanfu made it possible for women to connect with their cultural roots while also adapting to changing fashion trends. Today, Hanfu continues to inspire people across the world as a symbol of rich cultural heritage and traditional values that are still relevant even in modern times.

 Previous Post
Previous Post